Human Papillomavirus Vaccine Overview
The Human Papillomavirus Vaccine helps prevent various cancers and genital warts caused by HPV. It primarily targets reducing cervical, vulvar, and vaginal cancers in women, while also protecting against anal cancer and genital warts in both male and female.
Administration and Dosage
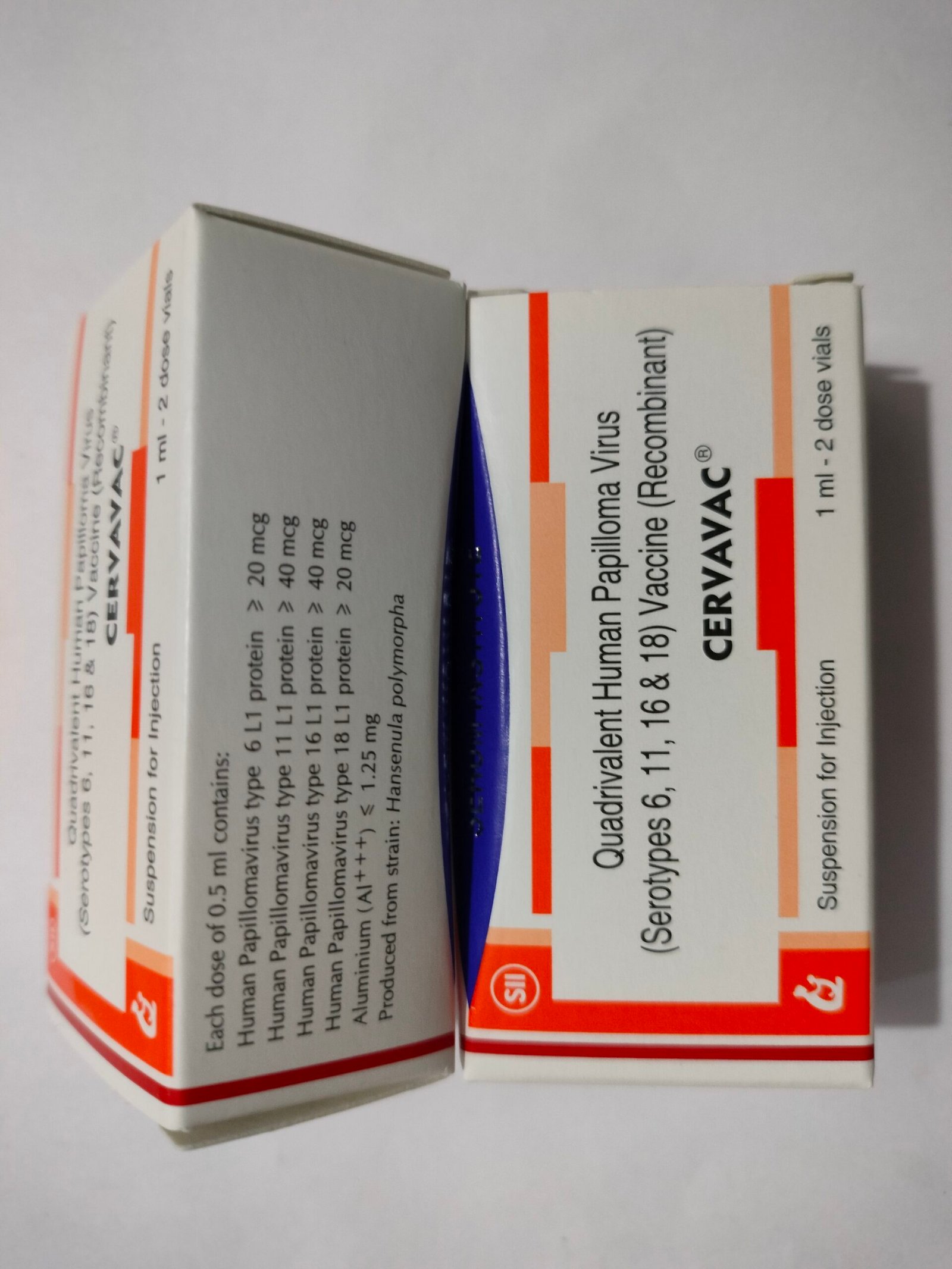
Healthcare professionals administer this vaccine via injection to females aged 9 to 45 years. Typically, it’s given in two or three doses, spaced several months apart. Adhering to the prescribed dosage and schedule is crucial for maximum effectiveness.
Benefits and Uses
The vaccine specifically prevents cervical cancer and pre-cancerous lesions caused by HPV types 16 and 18. By stimulating the body’s immune response, it strengthens immunity against these HPV strains, reducing the risk of associated cancers and lesions, as well as protecting against genital warts.
Side Effects and Precautions
Common side effects include mild discomfort, joint and muscle pain, headaches, and minor stomach upset at the injection site. While usually temporary, it’s essential to consult a doctor if they persist or worsen. Before vaccination, inform your doctor of any history of fainting with previous injections or a weakened immune system. Discuss the safety of vaccination during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Conclusion and Recommendations
The Human Papillomavirus Vaccine is crucial in combating HPV-related cancers and genital warts. Following the recommended vaccination schedule and maintaining regular screenings significantly reduce the risk of developing these conditions associated with HPV infection.
This content provides informational guidance and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized recommendations and treatment options.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.